Business Rule in ServiceNow

In the realm of IT Service Management (ITSM), ServiceNow stands out as a powerful platform that streamlines workflows, enhances collaboration, and boosts productivity. At the heart of ServiceNow’s capabilities lie its Business Rules, a critical component that drives automation and ensures efficient service delivery. In this blog, we delve into the significance of Business Rules in ServiceNow and explore how they contribute to organizational success.
What is business rule?
In ServiceNow, a business rule is a server-side script that runs when a record is displayed, inserted, updated, or deleted, based on the conditions defined in the rule. Business rules are a powerful tool used to automate processes, enforce policies, and maintain data integrity within the ServiceNow platform.
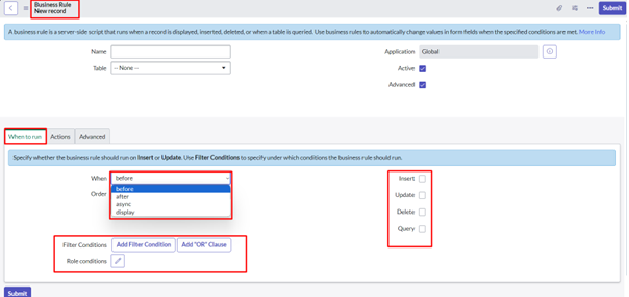
Types of Business Rules:
Basic Components of Business Rule:
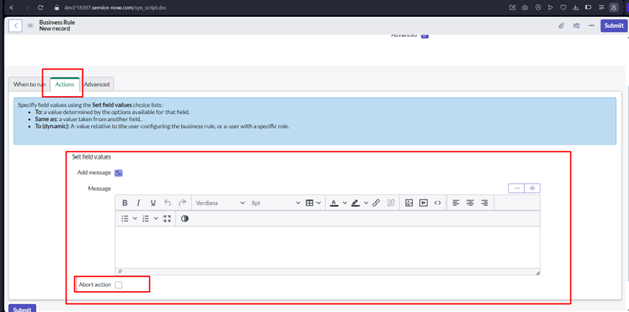
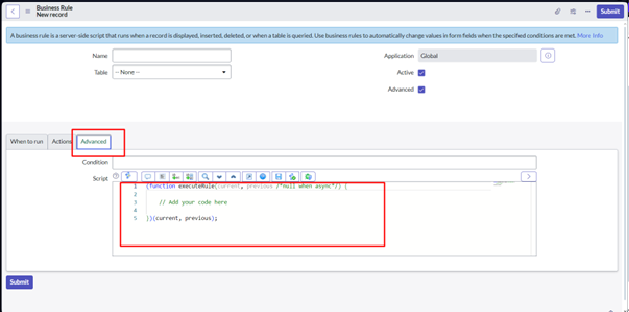
Conditions: Business Rules start with conditions that must be met for the rule to trigger. These conditions are defined using Glide Record queries, which specify the records to which the rule applies.
Script: The heart of a Business Rule is its server-side script. This script determines what actions should be taken when the conditions are met. It can modify data, display messages, log information, and more.
Order: Business Rules can have an order field, indicating the sequence in which they should run when multiple rules are applicable to the same condition. This allows for precise control overrule execution.
What are the importance of business rule?
Automation: Business Rules automate repetitive tasks and decision-making processes. This reduces manual intervention, minimizing the risk of human errors and improving efficiency.
Data Validation: Business Rules can be used to validate data before it is saved to the database. This helps maintain data integrity and accuracy.
User Experience: By using Business Rules to customize form behavior, you can create a more user-friendly experience. For instance, you can set field values, show or hide form elements, and display informative messages based on user inputs.
Process Flow: Business Rules can guide the flow of processes by automating task assignments, approvals, and notifications. This keeps processes on track and helps meet service level agreements (SLAs).
Few Use Cases of Business rule
Mandatory Fields: Ensure that essential fields are filled out before a record is saved to maintain data quality.
Populate Fields: Automatically populate fields on a form based on selections made by the user.
Approval Workflows: Trigger approval workflows based on specific conditions, such as the value of a requested item orthe category of an incident.
Notifications: Automatically sendnotifications to users or groups when certain conditions are met, such as escalating an incident to a higher-level support team.
What are the forms rule for using business rule?
- Use before business rule if you want to set any value
- Use before business query business rule to filter and recall the queries.
- Use after business rule to insert, update & delete the record.
- Use display business rule to fetch the data from client side by using g_scartchpad.
Conclusion:
Business Rules help make things work better in ServiceNow. They help automate tasks, apply rules, and improve how ServiceNow works. You can use them well by learning how they work and when to use them. This can help your organization manage IT services better. Business Rules can make tasks easier, data more accurate, and user experience smoother. This can make your ServiceNow instance more efficient and satisfying.
